Envio Developer Update April 2024

Welcome to the latest developer update of April 2024. Dive into our latest release V.0.0.40 and see what the Envio team has been shipping over the past month including new features and technical updates, upcoming events, developer tutorials and much more. 🚢
🚀 New Release: Version 0.0.40 Now Available! 🚀
- New Feature: Add custom indices to your database. (See guide below)
- New Feature: Reference your generated code as a package in your handlers. (See guide below)
- Our fast Hypersync Client Event Decoder now handles string types in events and will be the default event decoder used by the indexer. (To use Viem instead, you can set
event_decoder: viemin your config.yaml file.) - Fix: Failures on DB migrations now exit with failure code 1.
Envio HyperSync Expands Support on the Fuel Network

In addition, we’re excited to announce that Envio has recently fully integrated its Hypersync service on the Fuel Network, a Rollup Operating System purpose-built for Ethereum. Envio’s data infrastructure serves as an accelerated data query layer on top of the Fuel Network allowing application developers and data analysts to easily parse, query, and analyse large datasets on Fuel within seconds! ⚡
Check out Spark Finance, the world's fastest on-chain order book built on Fuel VM, is a great case study for utilising Hypersync to present near-instant access to order book information to their traders.
Learn more here.
New HyperSync Network Support ⚡
We’re excited to announce that Envio HyperSync has expanded enhanced indexing support for developers building on Polygon’s Amoy Testnet. ⚡
To see the full list of currently supported chains on HyperSync visit our docs.
⭐Note: This list is for Hypersync-supported networks only. Envio’s HyperIndex, as the indexing framework, supports any EVM network using RPC. If you would like Hypersync added to a network we don’t support, just let us know!
Create Custom Indices
Our new exciting feature allows developers to refine an entity and use the @index directive on fields they wish to add an index to.
type MyEntity {
id: ID!
userAddress: String! @index
tokenAddress: String! @index
}
The fields marked with @index will now create indices in your database, making querying on these fields much faster.
You can also group fields into one composite index like this:
type MyEntity @index(fields: ["userAddress", "tokenAddress"]) {
id: ID!
userAddress: String!
tokenAddress: String!
}
This will then create a composite index on both of these fields.
⭐Note: All id fields and @derivedFrom fields automatically have indices, so there is no need to add a custom index.
Reference Generated Code As a Package
⭐Note: This is optional and you should be able to continue referencing your generated files as before with no changes.
Previously, you would have to reference the file that gives you handlers and types in your generated folder like this:
import { ERC20Contract } from "../generated/src/Handlers.gen";
import { AccountEntity } from "../generated/src/Types.gen";
ERC20Contract.Transfer.handler(({ event, context }) => {...
Now you can add your generated code as an optional dependency in your project's package.json like this:
{
//... rest of package.json configuration,
"optionalDependencies": {
"generated": "./generated"
}
}
From there you can simply reference the functions and types like this:
import { ERC20Contract, AccountEntity } from "generated";
ERC20Contract.Transfer.handler(({ event, context }) => {...
For handler unit tests, simply import TestHelpers:
import assert from "assert";
import { TestHelpers, AccountEntity } from "generated";
const { MockDb, ERC20, Addresses } = TestHelpers;
describe("Transfers", () => {
it("Transfer subtracts the from account balance and adds to the to account balance", () => {
//Instantiate a mock DB
const mockDbEmpty = MockDb.createMockDb();
//Get mock addresses from helpers
const userAddress1 = Addresses.mockAddresses[0];
const userAddress2 = Addresses.mockAddresses[1];
//Make a mock entity to set the initial state of the mock db
const mockAccountEntity: AccountEntity = {
id: userAddress1,
balance: 5n,
};
Featured Developer🧑💻

This month's featured community member and developer of the month is Valentin Seehausen (AKA valle.xyz) an economist, blockchain developer and smart contact boot camp lead at the Frankfurt School. Valentin is an active contributor to our community and a next-level developer who has built three epic indexers using Envio for:
- TangleSwap, a non-custodial, multi-chain DeFi protocol.
- Peppy Finance, a decentralized perpetual exchange on Shimmer & IOTA.
- DegenSteaks, a prediction market for degens on Base.
For a full list of deployed indexers visit our explorer.
Follow Valle on X.
DappCon 2024 Sponsors

Incredibly excited to announce that Envio has been listed as one of the many proud sponsors of DappCon 2024! Hosted by Gnosis in Berlin, DappCon is an awesome developer conference for Ethereum infrastructure and dApps and is a great chance to get your project recognised and to learn from the very best, all while soaking in Berlin’s eclectic atmosphere.
Get your ticket here.
Upcoming Events 🗓️
- DAPPCON24: 21st - 23rd May, 2024
- ETHBerlin04: 24th - 26th May, 2024
- ETHCC Brussels: 8th - 11th July, 2024
Developer Workshops 🧑💻
Developer Tutorials:
Written Tutorials:
- LearnWeb3 - Indexing Greeter contract on Polygon and Linea using Envio
- LearnWeb3 - Indexing ERC-20 USDC Token Transfers on Base using Envio's HyperIndex
- LearnWeb3 - Indexing Optimism Bridge deposits using Envio's HyperIndex
For a full list of written tutorials visit our docs.
Envio 101 Video Tutorials:
- What is Blockchain Indexing?
- How to Set up a Blockchain Indexer | Part 1
- How to Modify your Blockchain Indexer | Part 2
- How to Index Factory Contracts | Part 3
- Extract Data 100x Faster than RPC | Uniswap V3 Factory Contract | Envio HyperSync Tutorial
- Fetch Every Uniswap V3 Pool Contract on Arbitrum in under 1 min | Envio HyperSync Tutorial
For a full list of our video tutorials visit our YouTube.
Previous Releases 🏗️
⭐Please note our current release is V0.0.40 🚀
Over the past month, we released three new versions of Envio (v.0.0.38 → v.0.0.40).
V.0.0.38
- Visualize your indexer progress easily in our hosted service.
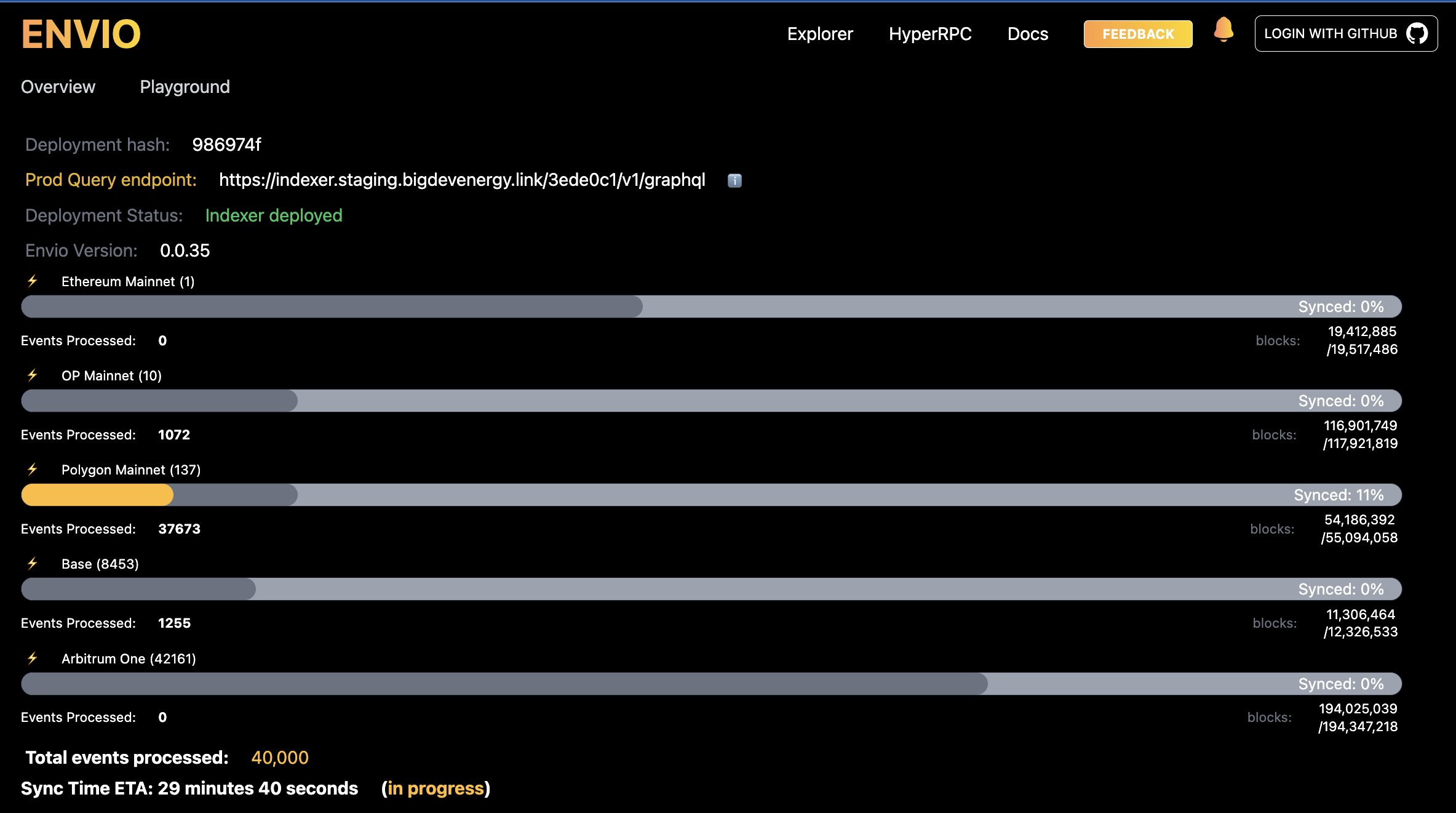
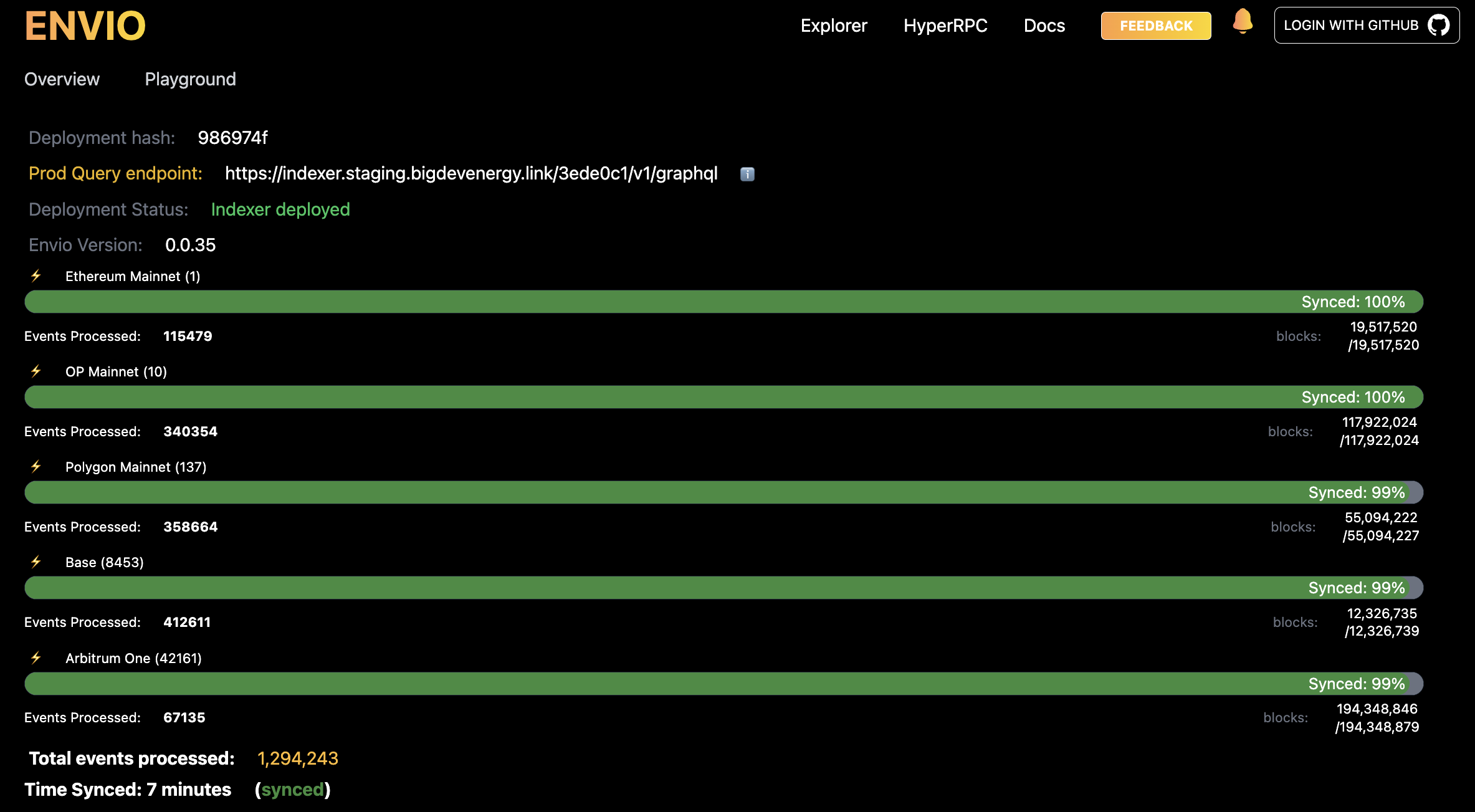
Fixes:
- Addressed an issue where the Hypersync client event decoder did not handle address checksumming.
⭐Note: While our Hypersync client event decoder is significantly faster, it remains optional as it currently lacks support for decoding string types in events. We're actively working on implementing this feature, after which it will automatically become the default decoder for the indexer. In the meantime, you can opt-in by adding event_decoder: hypersync-client to your configuration.
V.0.0.39
Patch updates:
- New HyperSync support for Poylgon’s Amoy Testnet.
- Improves crash error logs when deploying to the hosted service & fixes the false error produced by yoga package on the TUI in the instance of an indexer crash.
Playlist of the month
Got any questions, or have any feedback? We’re all ears! Hop in our Discord and let us know, we’d be happy to help and always appreciate feedback of any kind to improve your developer experience.
Stay tuned for more monthly updates by subscribing to our newsletter, following us on X or hopping into our Discord for more up-to-date information.
About Envio
Envio is a fast, developer friendly blockchain indexer and the fastest, most flexible way to get on-chain data, making real-time data accessible for developers across the Web3 ecosystem.
With Envio, developers can query and stream blockchain data efficiently without the complexity of running their own infrastructure. Envio’s blockchain indexing tools supports any EVM network and is trusted by many teams building everything from DeFi platforms to analytics dashboards and production applications.
If you’re a blockchain developer or analyst looking to enhance your workflow, look no further. Join our growing community of Web3 builders and explore our docs.