What is a blockchain indexing?

It’s no secret that blockchain indexing solutions can free up development resources, reduce time to market, and improve the overall end-user experience. Imagine you're a developer building a decentralized application (dApp) that requires real-time access to on-chain data, user interactions, and smart contract events. Navigating this ocean is a complex task and can be like searching for a needle in a haystack.
Since a blockchain acts as a distributed database and a smart contract is a dApp that works with a blockchain, it's important to know that smart contracts aren't just the backend of the application. Through the JSON-RPC API users can call smart contracts on the blockchain, triggering them to be executed with given parameters. Users can also view data from the blockchain. Asking for information about a particular block or account from the blockchain is quite a simple task. But when we want to get data from many blocks at once, it's more complicated because we need to aggregate data from multiple single-block queries.
Blockchain data is designed to be written in a sequence, one block after another, as the chain is made, leaving data scattered, unorganized, and under-utilized. It can be a slow process to retrieve (or commonly referred to as “sync”) larger datasets, some taking up to a few days or weeks. More advanced dApps require more data processing logic (e.g. SUM, AVG, multi-chain, etc.) this immediately adds additional code to your dApp, and slows down responsiveness.
This is where blockchain indexers like Envio come into play as specialized infrastructure tools that streamline the process of categorizing and indexing blockchain data. In this article, we'll dive into the concept of blockchain indexers, their core components, and how they improve the developer experience.
What is a blockchain indexer?
A blockchain indexer is a tool that pulls raw data from a node, organises it into structured tables, and gives developers a clear and fast way to view and work with on chain activity. Similar to the index of a book, it takes complex on chain data and organises it so developers can query, retrieve, and use that data without digging through a full node.
Developers only need to define data types and the relationships between them according to the smart contract, and how this data should be stored. The indexing solution then provides a custom GraphQL endpoint to easily present this data for your dApp, while taking care of the rest. By doing so, indexers enable developers to retrieve and process advanced data efficiently, ultimately boosting productivity and allowing more time to focus on the application.
A key advantage of using a powerful blockchain indexing solution like Envio is its ability to abstract the complexity of managing your own infrastructure while keeping costs lower. Indexing solutions are built for low latency and fast access to historic data. With a reliable indexer, you can retrieve filtered data in seconds or minutes, work that would take days or even weeks if you relied only on RPC JSON requests.
What are the fundamental components of a blockchain indexer?
As a developer, you can define which blockchain data is being indexed and how it is stored. It is important to note, that some indexing solutions differ in their configuration, but a typical Indexer definition consists of three files:
- config.yaml
- schema.graphl
- event handlers
🧭 Configuration: A configuration file, often named config.yaml, houses essential settings for your indexer. These settings encompass many details including smart contract addresses, blockchain networks, RPC (Remote Procedure Call) endpoints, start blocks, and ABI (Application Binary Interface) paths and events to pay attention to.
Here’s an example of a config.yaml file for indexing a live Greeter smart contract example deployed on Polygon.
name: Greeter
description: Greeter indexer
networks:
- id: 137 # Polygon
rpc_config:
url: https://polygon.llamarpc.com # We recommend you change this to a dedicated RPC provider
start_block: 45336336
contracts:
- name: Greeter
abi_file_path: abis/greeter-abi.json
address: "0x9D02A17dE4E68545d3a58D3a20BbBE0399E05c9c"
handler: ./src/EventHandlers.bs.js
events:
- event: "NewGreeting"
requiredEntities:
- name: "User"
- event: "ClearGreeting"
requiredEntities:
- name: "User"
🏗️ GraphQL Schema: The GraphQL schema file (e.g., schema.graphql) outlines your application's data model. It defines the available data types that directly correspond to database tables, and the event handlers you create are responsible for creating and updating records within those tables. Additionally, the GraphQL API is automatically generated based on the entity types specified in the schema.graphql file, to allow access to the indexed data. Here's example schema from the live Greeter Contract contract:
type User {
id: ID!
latestGreeting: String!
numberOfGreetings: Int!
}
⚙️ Event Handlers: Event handlers (e.g., handlers.js) are components or functions designed to detect specific events on a blockchain. When these events occur, the handlers respond by executing predefined actions, creating or updating records in the database. Example of Event Handler function for the ‘NewGreeting’ event in the live Greeter Contract contract:
let { GreeterContract } = require("../generated/src/Handlers.bs.js");
GreeterContract.NewGreeting.handler((event, context) => {
let existingUser = context.greeting.get(event.params.user.toString());
if (existingUser != undefined) {
context.user.set({
id: event.params.user.toString(),
latestGreeting: event.params.greeting,
numberOfGreetings: existingUser.numberOfGreetings + 1,
greetings: [...existingUser.numberOfGreetings, event.params.greeting],
});
} else {
context.user.set({
id: event.params.user.toString(),
latestGreeting: event.params.greeting,
numberOfGreetings: 1,
greetings: [event.params.greeting],
});
}
});
These Indexer files are referred to as the “ user inputs” files in the diagram below. The diagram below provides a conceptual design of Envio’s indexing service.
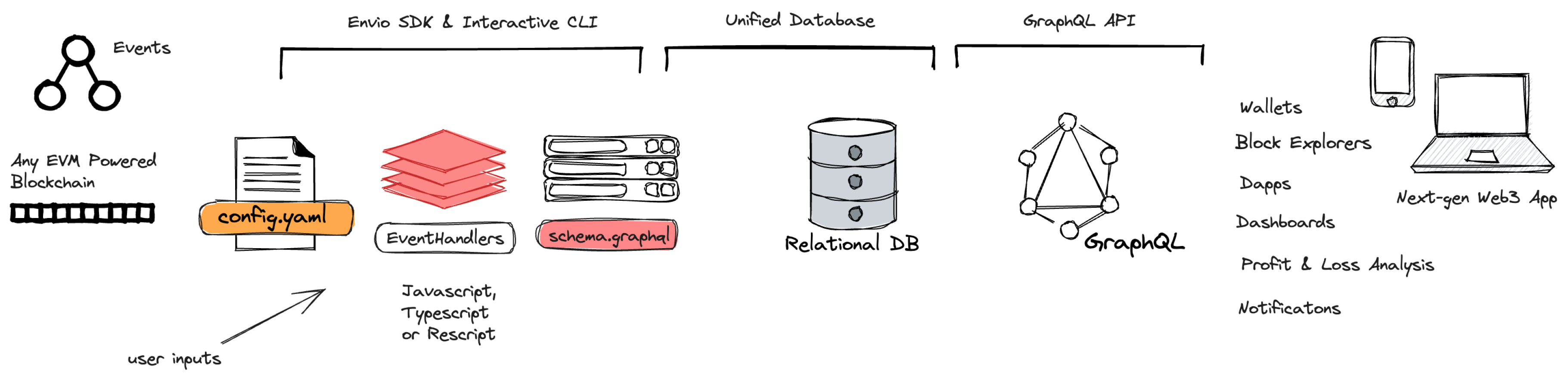
For testing purposes, the developer flow usually allows developers to host an indexer locally, before deploying to a hosted service. Some indexing solutions, like Envio, have an integrated testing framework, which increases confidence and reliability by allowing developers to test whether the defined data is being handled as expected using mockable events and expected outcomes.
Why blockchain indexers play a crucial part in dApp development?
Blockchain indexing solutions like Envio offer a myriad of benefits, from speeding up the dApp development lifecycle to increasing the responsiveness and reliability of your dApp for a smooth user experience. Here are a few reasons why blockchain indexing solutions play a critical role in the dApp development process:
-
Developer friendly: Blockchain indexing solutions make a dApp development easier by abstracting away a lot of the complexities that come with coding data logic and hosting your infrastructure, saving developers a lot of time to focus their efforts on the application. The developer flow of indexing solutions is mostly interactive and automated, with templates and helpful developer quickstart guides to start. In addition, some indexing solutions support familiar development languages such as JavaScript/ TypeScript for data handling, allowing quick onboarding, and testing frameworks for increased confidence.
-
Customizability: Indexing solutions allow developers to index application-specific data, such as custom events from contract functions. Standard template blockchain data APIs do not support the rich indexing capabilities that indexing solutions can offer. Whether you're launching a multi-chain NFT marketplace, starting a DAO, diving into GameFi, or pioneering the next big P2E project, Indexers serve as an essential building block tailored to your application’s unique data needs.
-
Multichain support: Some indexing solutions have multi-chain support, which aggregates data from multiple sources into a unified database table, making it super easy to present aggregated information in your front end for your multi-chain blockchain application. Developers do not need to worry about building multiple APIs or subgraphs and managing multiple databases.
-
Managed service: Indexing solutions offer free and paid production-grade hosted service options with guaranteed uptimes, ensuring that data access is always available and complete. Depending on the provider, the system architecture of the hosted service ensures performance is always consistent, providing a trustworthy and reliable solution to access real-time or historic blockchain data. Developers can focus on their front-end applications while indexing solutions guarantee performance and production-grade infrastructure.
-
Expert Support: It’s in the indexing provider’s best interest to provide a reliable service, with most solutions offering direct support channels with technical engineers and subject matter experts to help you with any issues or indexing-related needs.
About Envio
Envio is a fast, developer-friendly blockchain indexer and the fastest, most flexible way to get on-chain data, making real-time data accessible for developers across the Web3 ecosystem.
With Envio, developers can query and stream blockchain data efficiently without the complexity of running their own infrastructure. Envio’s blockchain indexing tools supports any EVM network and is trusted by many teams building everything from DeFi platforms to analytics dashboards and production applications.
If you’re a blockchain developer or analyst looking to enhance your workflow, look no further. Join our growing community of Web3 builders and explore our docs.